Compare 10 offers
Breaking Down the Anatomy of an Inverter in Renewable Energy Systems
Key Components and Functions of an Inverter
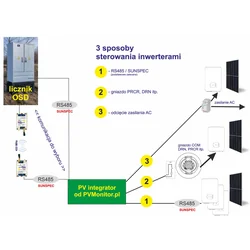
An inverter, a crucial element in renewable energy systems, serves to convert direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC). Its primary components include a DC input, power switches, transformers, and control circuits. The DC input connects to renewable sources, such as solar panels or wind turbines. Power switches manage current flow while transformers adjust voltage levels to match grid requirements. Control circuits oversee the entire operation, ensuring efficient energy conversion and synchronization with the grid.
Inverter Types: String vs. Micro
E-commerce businesses can broadly classify inverters into two categories: string inverters and microinverters. string inverters, suited for larger-scale installations, connect multiple solar panels in a series. These inverters are cost-effective but less flexible when dealing with shading or panel degradation issues. microinverters, on the other hand, attach to individual panels, offering enhanced performance monitoring, optimal energy harvesting under various conditions, and better fault tolerance, albeit at a higher cost.
Inverter Selection Criteria for B2B Customers
Professionals choosing inverters for renewable energy systems need to consider efficiency, cost, reliability, and compatibility with their specific system. Top-tier manufacturers ensure high-quality components, rigorous testing, and extended warranties, which contribute to long-term return on investment. Additionally, obtaining certification from independent organizations like the California Energy Commission (CEC) offers a performance benchmark and ensures compliance with industry standards.